Glossary
-
&
- AUTO-ANGULAR CALIBRATION: The Auto-Angular Calibration is performed by the scanner. It applies a correction to the collimation error, i.e., the deviation of the Horizontal Axis (HA), or Vertical Axis (VA), or Sight Axis (SA).
-
&
- AUTO-DISTANCE CALIBRATION: The Auto-Distance Calibration is performed by the scanner. It applies a distance correction in the albedo measurement and the distance measurement.
-
FIRST SCAN AUTOMATIC ORIENTATION: This step is always applied to the first captured scan. It consists in finding the correct orientation of the captured data. At the end of the step, a notification pops up and summarizes the state of the step (succeeded (Green) or failed (Red)).
-
AUTOMATIC REGISTRATION: The Automatic Registration is always enabled and works with pairwise scans or pairwise registration sets. When the Automatic registration is launched, it computes a transformation to fit the current scan with the previous one (default mode) (A), or with a chosen one (B) as perfect as it can. It can also compute no transformation (C).
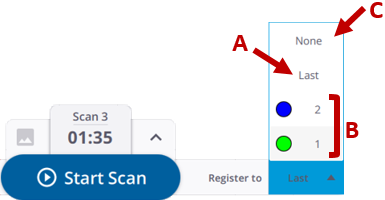
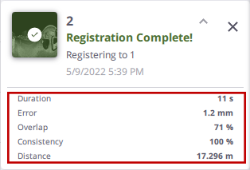
After each Automatic registration, some statistics are computed. The computed statistics and the resulting notification are here to help you inspect the transformation but do not replace a human control.
-
CONSISTENCY (%): This gives an idea of how reliable a pair (of registered stations) is. It is expressed in percentage.
- DISTANCE: This refers to the distance between two registered stations (from station position to station position).
-
- FIELD CALIBRATION: The Field Calibration refers to both the Auto-Angular Calibration and the Auto-Distance Calibration.
-
HDR (High Dynamic Range): When the mode is On, the scanner captures two additional images (one darker and one brighter) when it captures an image, and mashes them together to create a single image with more color and detail in both the bright and dark areas.
-
JSON: It's a lightweight file in JavaScript Object Notation format that enables interchanging data.
-
- DIAGNOSTIC: This feature consists in running a series of tests in the scanner. Tests are subdivided as follows:
- Information Tests: Firmware, temperature value, etc.
- Sub-part Detection Tests: Presence of memory card, IMU, etc.
- Advanced Tests: Deflection, Auto-calibration distance, Auto-distance calibration, etc.
Results are not displayed with values but with colors: Green (Pass) and Red (Fail).
- LINK: The Link refers to the registration link(s) from a registered station.
-
OVERLAP (%): The Overlap (%) refers to the amount of common points per pair (of registered stations) in percentage. The percentage in a pair (of registered stations) is the same from one direction to the other (e.g. from Station_A to Station_B or from Station_B to Station_A).
- REGISTRATION: A Registration consists in applying a transformation to the current scan so that it fits as much as possible to the previous station or to a chosen station, whatever the method (automatic or manual). The goal is to have your project completely registered from the first scan to the last one, meaning that all stations reside in a unique registration set.
-
RMS ERROR: The RMS Error refers to the root mean square of the point-to-point distances on the overlapping areas. It is computed from the distances between individual points in the first scan to their corresponding scan point in the second scan. The error is symmetrical; it has the same value from Station_A to Station_B as from Station_B to Station_A.
-
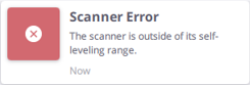
- SELF-LEVELING: This option is by default on. It consists in measuring the horizontality and verticality of the scanner. If the scanner is within a range of +10° and -10° from either side of its vertical axis, the captured stations are Leveled. If the scanner is within the following ranges, from +10° to +45° and from -10° to -45°, from either side of its vertical axis, the captured stations are Not leveled. If the scanner is out of the operating ranges, i.e., greater to +45° and -45° from either side of its vertical axis, the software displays an error and then prevents you from collecting the data.
-
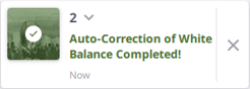
WHITE BALANCE: This is a process that a camera uses to remove color casts produced by the different color temperatures, so that white objects appear white in the pictures.
In the Auto mode, the white balance correction is disabled in the scanner. The images are captured with no correction. The correction is applied to the images in the software once they are downloaded (a notification pops up once the correction is applied).
With the other modes, the images are directly corrected once captured by the scanner (no notification popped-up by the software).