Compute point
To calculate the coordinates of an intersection point from one or more points, a line, or an arc:
- Tap
and select Cogo / Compute point and then select the method to use for the calculation.
-
Enter the name of the point and, if required, the code for the point.
-
Define the new point as required for the selected method.
TIP –
- When selecting reference points, select them from the map or tap
for other selection methods. See To enter a point name.
- To change how distances are calculated, tap Options. See Cogo settings.
 Bearing and distance method
Bearing and distance method
- Select the start point (1).
-
In the Start point field, tap
to select the Radial or Sequential measurement method.
When Sequential is selected, the Start point field is automatically updated to the last stored intersection point.
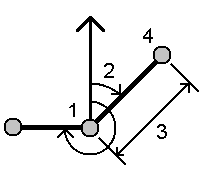
Radial
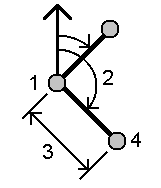
Sequential:
- Set the Azimuth origin to Grid 0°, True, Magnetic, or Sun (GNSS only).
-
Enter the azimuth (2) and the horizontal distance (3).
To adjust the azimuth value:
- In the Azimuth field, tap
to adjust the azimuth by +90°, ‑90°, or +180°.
- Enter a value in the Delta azimuth field. The Computed azimuth field displays the azimuth adjusted by the delta azimuth.
- In the Azimuth field, tap
- Tap Calc. The software calculates the intersection point (4).
-
Tap Store.
 Turned angle and distance method
Turned angle and distance method
- Select the start point (1).
-
In the Start point field, tap
to select the Radial or Sequential measurement method.
When Sequential is selected, the Start point field is automatically updated to the last stored intersection point. The reference orientation for new points moving forward is the computed reverse azimuth from the previous turned angle.
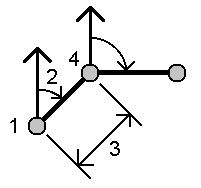
Radial:
Sequential:
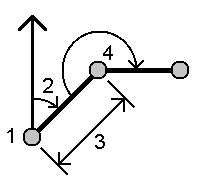
- To define the reference orientation:
- Select the End point. Alternatively, tap
in the End point field and select Azimuth and then enter the azimuth (2).
- Enter the Turned angle.
- Select the End point. Alternatively, tap
- Enter the horizontal distance (3).
- Tap Calc. The software calculates the intersection point (4).
-
Tap Store.
 Bearing-distance intersection method
Bearing-distance intersection method
-
Select point 1 (1) and point 2 (3), and enter the azimuth (2) and the horizontal distance (4).
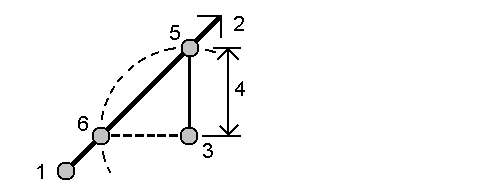
- Tap Calc. There are two solutions (5,6) for this calculation.
- To view the second solution, tap Other.
- Tap Store.
 Bearing-bearing intersection method
Bearing-bearing intersection method
-
Select point 1 (1) and point 2 (3), and enter the azimuth from point one (2) and point two (4).
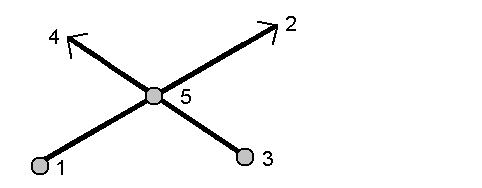
- Tap Calc. The software calculates the intersection point (5).
- Tap Store.
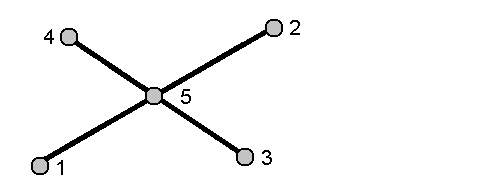
 Distance-distance intersection method
Distance-distance intersection method
-
Select point 1 (1) and point 2 (3), and enter the horizontal distance from point one (2) and point 2 (4).
- Tap Calc. There are two solutions (5,6) for this calculation.
- To view the second solution, tap Other.
- Tap Store.
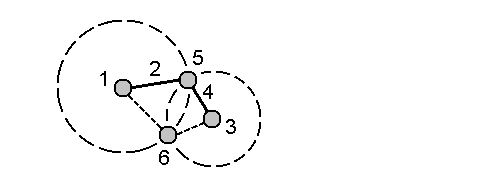
 Four-point intersection method
Four-point intersection method
-
Select the start point of line 1 (1), the end point of line 1 (2), the start point of line 2 (3) and the end point of line 2 (4).
- Enter any change in the vertical position as a vertical distance from the end of line 2.
-
Tap Calc. The software calculates the offset point (5).
The two lines do not have to intersect, but they must converge at some point, as shown below.
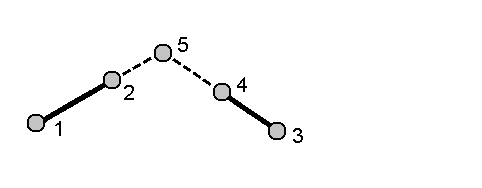
- Tap Store.
NOTE – If you use the Four point intersection method or the From a baseline method and then change the antenna height record for one of the source points, the coordinates of the point will not be updated.
 From a baseline method
From a baseline method
-
Select the start point (1) and the end point (2) of the baseline.
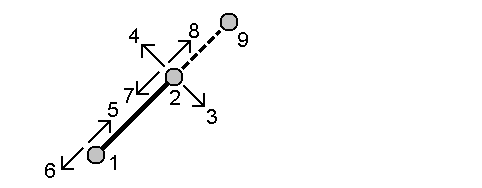
- Enter a Distance and select the Distance direction method (5, 6, 7, or 8).
- Enter the offset distance and select the Offset direction(3 or 4).
-
Enter the vertical distance.
The vertical distance is dependent on the Distance direction. If the direction is relative to the start point, the elevation of the computed point is the elevation of the start point plus the vertical distance. Similarly, if the direction is relative to the end point, the elevation of the computed point is the elevation of the end point plus the vertical distance.
- Tap Calc. The software calculates the offset point (9).
NOTE – If you use the Four point intersection method or the From a baseline method and then change the antenna height record for one of the source points, the coordinates of the point will not be updated.
 Project point to line method
Project point to line method
To compute a point at a position along a line that is perpendicular to another point:
-
Enter the Point to project (1).
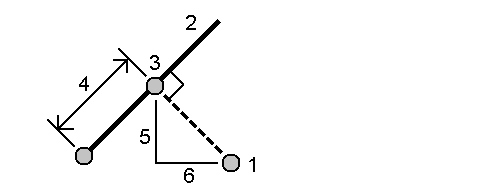
- Enter the Line name(2) or select the Start point and End point to define the line.
-
Tap Calc.
The software calculates the following values:
- coordinates of the point (3)
- horizontal distance along the line (4)
-
horizontal and slope distance, azimuth, grade, vertical distance, and delta north (5) and east (6) values from the selected point (1) to point (3)
- Tap Store.
 Project point to arc method
Project point to arc method
To compute a point at a position along an arc that is perpendicular to another point:
-
Enter the Point to project (1).
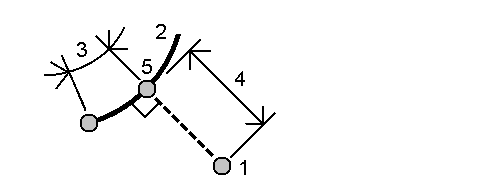
- Enter the Arc name or key in a new arc.
-
Tap Calc.
The software calculates the following values:
- coordinates of the point (5)
- horizontal distance along the arc (3)
-
horizontal distance from the arc (4)
- Tap Store.
- When selecting reference points, select them from the map or tap