Surface scanning
Use surface scanning to scan surfaces when connected to a Trimble S Series total station that does not have Trimble VISION technology. If the connected instrument has Trimble VISION technology or is a Trimble SX10 or SX12 scanning total station, see Scanning.
- From the Survey menu, select Surface scan.
- Enter the Start point name and Code.
- In the Method field, select a measurement method.
- Define the area for the scan and grid interval using one of the methods described below.
-
Tap the Instrument icon in the status bar to open the Instrument functions screen and set the EDM measurement method (TRK is fastest).
The total number of points to scan, scan grid dimensions, and estimated scan time are displayed. Change the scan size, step sizes or EDM measurement method to increase or decrease the number of points and scan time.
- Tap Start.
To define the scan area
To define the scan area, do one of the following:
- If the point already exists, enter the point name, or use menu arrow to select it from the list.
- From the pop‑up menu in the Top left and Bottom right fields select Fast fix or Measure to measure and store points that define the limits of the search.
Define the scan area with one of the following methods.
The defined scan area may not exactly fit the grid interval. There may be an area left over along the scan extents that is smaller than the grid interval. If the width of this area is less than one‑fifth of the grid interval, the points along this scan area will not be measured. If the width is more than one‑fifth of the grid interval, then an extra point is scanned.
Use this method on complex surfaces when you cannot use a rectangular plane to approximate the surface you are scanning.
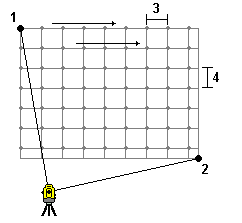
- Aim to the top left corner of the scan area (1) and measure a point.
- Aim to the bottom right corner of the scan area (2) and measure another point.
- Define the angular grid interval, where:
3 is the Horizontal angle
4 is the Vertical angle
To define a Horizontal only scan of a 360° scan area, set the Top left and Bottom right points to the same name, and set the VA interval to null.
Use this method on a plane surface where you need a regular grid interval. The Trimble Access software determines the angle of the plane, and uses this and the grid interval to approximate how far to turn the instrument for each subsequent point.
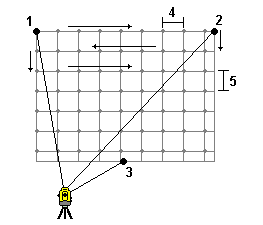
- Aim to the first corner of the scan area (1) and measure a point.
- Aim to the second corner of the scan area (2) and measure another point.
- Aim to the third point on the opposite side of the plane (3) and measure a point.
- Define the distance grid interval, where:
4 is the horizontal distance
5 is the vertical distance
Use this method to define the area to scan from a centerline that has equal offsets to the left and right. The Trimble Access software defines the surface using horizontal offsets perpendicular to the centerline. The software then uses this definition and the station interval to determine approximately how far to turn the instrument for each subsequent point.
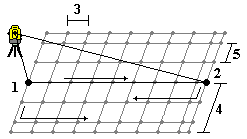
- Do one of the following:
- Two point method:
- Aim to the start point of the centerline (1) and measure a point.
- Aim to the end point of the centerline (2) and measure another point. These two points (1 and 2) define the centerline.
- Access the pop‑up menu in the Start point field. Change the method and then define the line by a start point with azimuth and length.
- Define the station interval (3).
- Define the maximum offset distance (4).
- Define the offset interval (5).
The Trimble Access software scans the centerline first, then the points on the right‑hand side, and finally the left‑hand side.