Workflow Overview
-
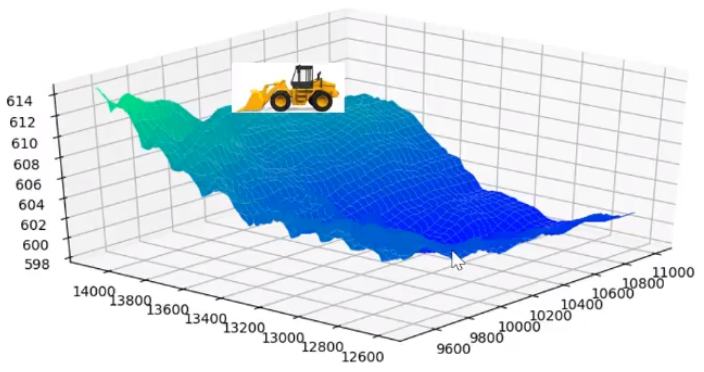
Using your machine control system’s GPS/GNSS data, WorksOS accurately maps the locations and elevations of every place your machines work within your project’s boundaries.
-
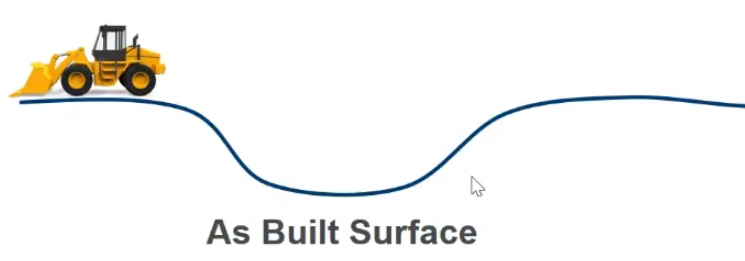
From that data, you can ‘create’ an as-built surface, which is the last pass of a machine creating the final surface of the day. This is done by refining the raw machine surface in WorksOS to create a more finished (i.e., filtered) version. The ability to refine an existing as-built surface is the power of WorksOS; they convert raw data into something you can use to plan. Filters provide you surfaces for specific dates (filter), machines (filter), and design/area/alignment (filter), etc.
-
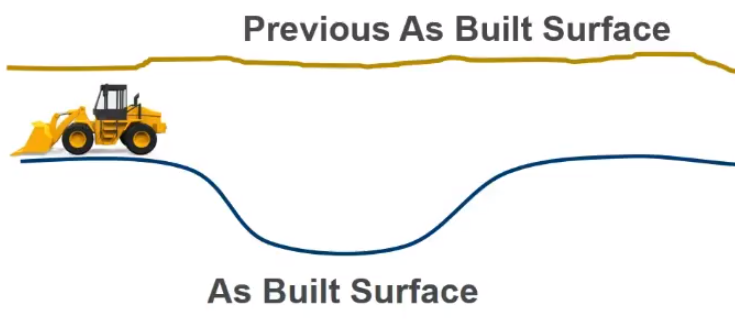
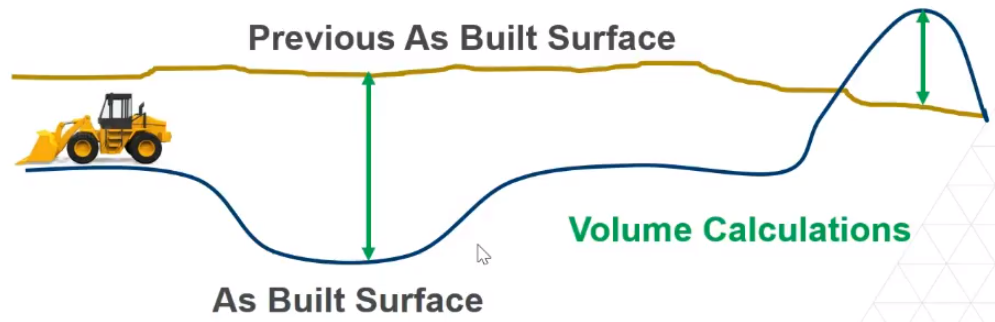
Now you can compare that last as-built surface to a previous as-built surface.
-
Based on the change/difference between the two surfaces, you can calculate volumes.
-
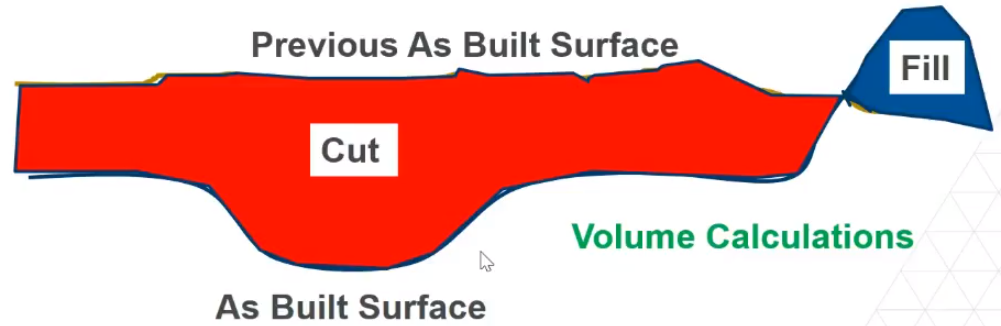
Anywhere the elevation of the design surface is below the current surface is ‘in cut’; anywhere the design is above the existing is ‘in fill’, so you can also create cut/fill maps.
-
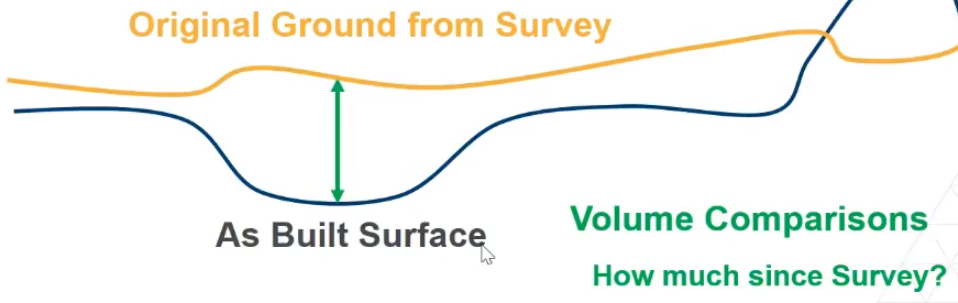
In addition, you can compare the as-built surface to the original ground surface from a survey. This volume comparison tells you how much work has been done since the original survey.
-
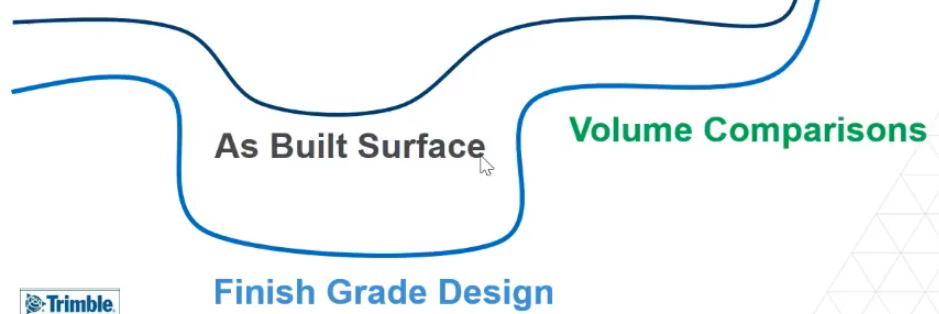
You can also import design surfaces from Trimble Business Center (TBC) to help determine how much work remains to achieve the design.
-
If you also pull in linework and geofences from TBC, and compare them to the finish grade design, this will tell you how much work is remaining to complete.
-
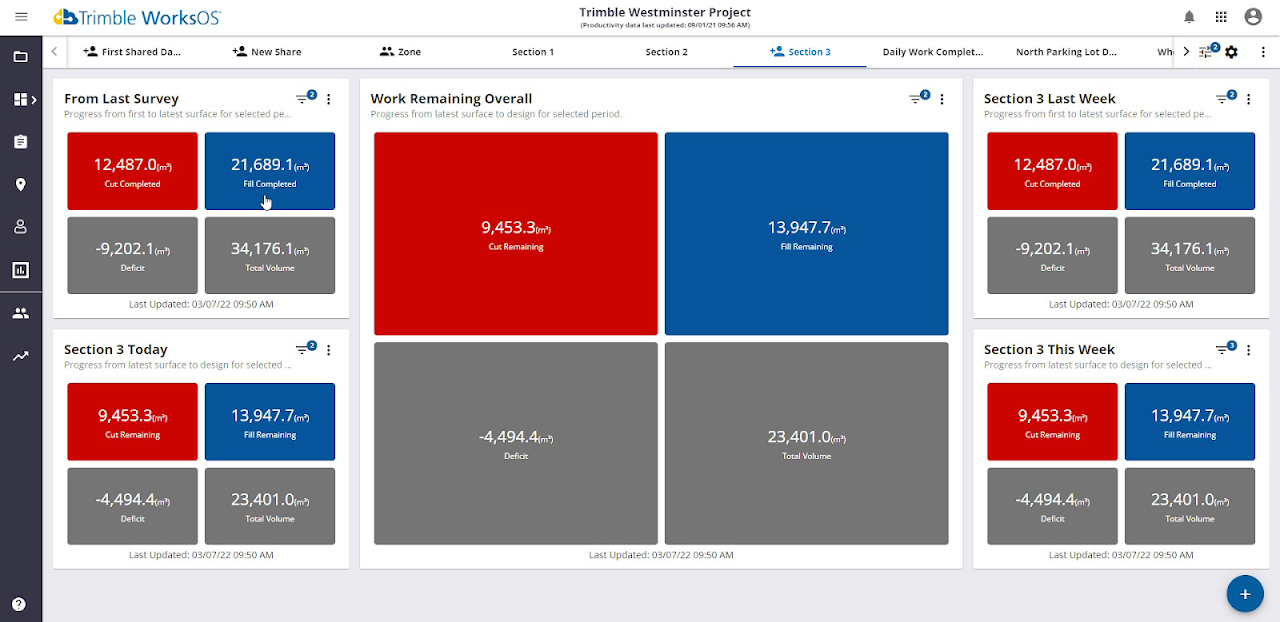
To see all of your cut/fill, compaction, and other data in one place, visit your configurable Dashboard where you can set up various widgets for a quick look at the movement of material, work completed since the initial survey, and work remaining to get to the finish grade.