About the Trimble xFill service
xFill is a service that extends RTK positioning for several minutes when the RTK correction stream is temporarily unavailable. The xFill service improves field productivity by reducing downtime waiting to re-establish RTK corrections in black spots. It can even expand productivity by allowing short excursions into valleys and other locations where continuous correction messages were not previously possible. Proprietary Trimble xFill corrections are broadcast by satellite and are generally available on construction sites globally where the GNSS constellations are also visible. It applies to any positioning task being performed with a single-base, Trimble Internet Base Station Service (IBSS), or VRS™ RTK correction source.
To maintain centimeter positioning with GNSS signals, the xFill service provides a specialized correction stream broadcast by MSS-band satellite that is generated using Trimble Real-time eXtended (RTX™) technology.
Trimble RTX technology to support xFill
The general infrastructure of the RTX system is shown in the following schematic flowchart.
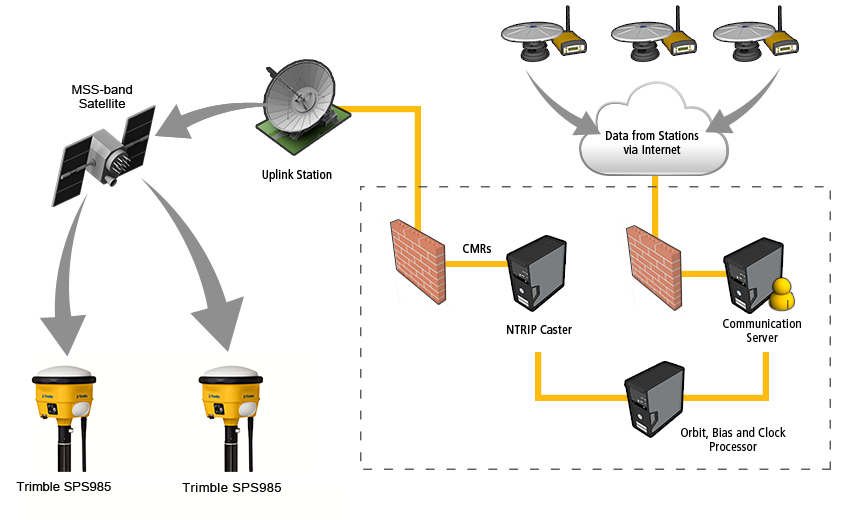
The precise satellite data generated by the network processors are compressed in messages then routed to a satellite uplink station.
The Trimble RTX tracking network currently comprises approximately 100 stations that are distributed across the globe.
About xFill
Most RTK systems currently rely on radio or cell phone (using the internet) connections to receive corrections from a reference station. The reference station in this case could be a single physical station, familiar to GNSS surveyors as traditional single-baseline RTK, or a VRS RTK correction source such as a single base, Trimble Internet Base Station Service (IBSS), or Virtual Reference Station such as Trimble VRS Now.
Trimble xFill technology aids standard RTK systems in the event of connection outages with the primary source of corrections. The signal outage takes place at the rover locations where the building is between the user and the reference station radio transmitter, effectively blocking the signal and causing a suspension of RTK positioning. The same scenario can occur when an RTX user moves to area where a large building or hill blocks communication with the active cellular tower.
Trimble xFill is not a stand-alone positioning service but instead uses the RTX infrastructure to augment standard RTK methods. The multitude of GNSS correction streams now available for Trimble RTK users with the introduction of Trimble xFill is shown in the following figure.
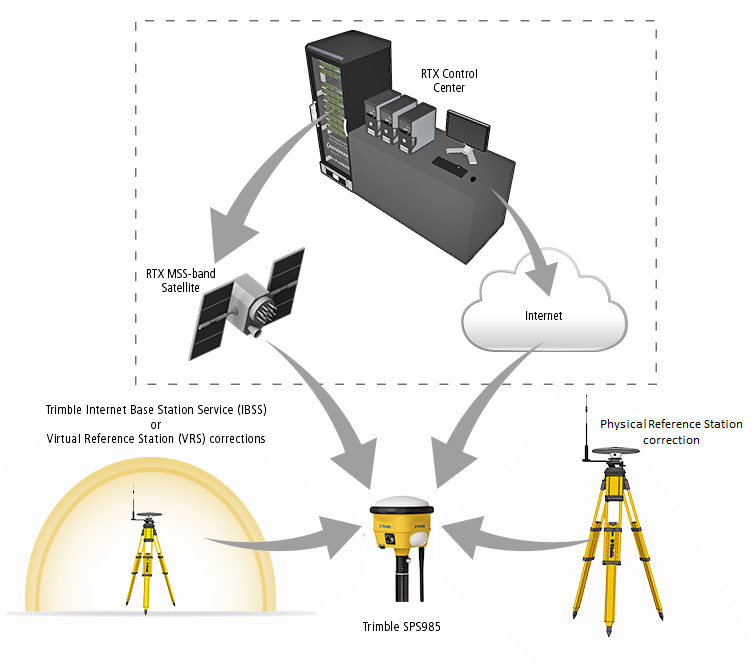
In areas of Trimble RTX satellite coverage, the GNSS receiver operates with the simultaneous input of the original correction stream and the Trimble xFill stream. In the event of a correction outage, the Trimble xFill corrections provide the mechanism to maintain high precision RTK positioning based on just the rover GNSS observables. This “fills the gap” caused by the primary correction stream outage (hence the feature name “xFill”).
As a result of the Trimble xFill corrections being transmitted over an independent link (an MSS-band satellite beam, rather than the base station radio); they will typically remain available when the reference station correction is missing. Terrestrial radio signals are often blocked, leaving a good view of the GNSS satellites and the Trimble xFill MSS-band beam. The multi-GNSS capabilities of the GNSS receivers further improves the ability to track sufficient satellites for Trimble xFill operation in obscured environments. The receiver is able to continuously receive RTK positions as it crosses the radio shadow area.
The rover will continue to receive the Trimble xFill signal as long as line-of-sight is maintained to the MSS-band satellite. Therefore, the signal is able to fill the gap and maintain RTK data processing.
In summary, the Trimble xFill technology enables GNSS users to dramatically extend their productivity in areas where the primary correction signal is poor. It does this by maximizing system availability when the Trimble xFill signal is available.
Performance of xFill
Trimble xFill is instantly available as soon as the RTK radio signal is lost. There is no delay due to, for example, a short convergence phase similar to the situation when RTK is first started. Trimble xFill is available to sustain RTK operation the same instant that the primary correction stream is lost—seamlessly filling the gaps that would otherwise have occurred. Trimble xFill is available as soon as the first regular RTK position has been reported to the rover.
The actual performance depends on satellite visibility, geometry, and the local multipath environment at the rover. Once Trimble xFill is active, the error growth is slow and largely linear; it will be represented by an increase in the reported precisions. Therefore, no special field procedure is necessary. If the primary correction source cannot be re-established, when the precision exceeds the user-specified tolerance the point will no longer be stored automatically. As soon as primary corrections resume, even for a second, the precisions are effectively “reset” to the level reported before switching to Trimble xFill (depending on any change to the satellite visibility). Even very sporadic radio reception could have little impact on the reported RTK precisions. Difficulty may occur only with longer outages. Currently, the GNSS receivers will continue to provide Trimble xFill positioning for up to five minutes following RTK outage.
Optimum performance also requires continuous tracking of the GNSS signals, which may not be possible when the signals are obstructed together with the primary correction broadcast. This can occur, for example, when operating very close to buildings. New satellites are always added to the Trimble xFill position solution, and those experiencing tracking interruptions and cycle-slips are introduced back into the solution. However, the temporary loss of GNSS signals can increase the precision growth if the satellite geometry is weakened. This is usually known as an increase in Position Dilution of Precision (PDOP), and it affects all GNSS positioning methods (it is not specific to Trimble xFill). When the number of tracked satellites falls below four, the Trimble xFill solution will terminate until the radio link is re-established and five satellites are visible. (The number may depend on the combination of GNSS satellites tracked when less than five GPS satellites are available.) This is similar to regular RTK, which requires a minimum of four satellites. However, the Trimble processing engine integrated in the GNSS receivers will ensure a rapid convergence to precision accuracy once five satellites are visible.
Using Trimble xFill
When the RTK correction stream is lost, the software automatically switches from RTK to Trimble xFill. The transition is immediate and completely seamless. When Trimble xFill is active, the software displays “xFill” in the status bar along with the estimated precisions.
Point measurement is available until the precision values exceed the user-defined tolerances. Once the precisions have exceeded the specified tolerances, the software will indicate that the precision of the position is outside of the user-defined tolerance. At that time, the user must restore the RTK correction stream to continue working at precision accuracy.
Characteristics of xFill
The following table summarizes the characteristics of xFill:
|
Trimble xFill characteristics |
|
|---|---|
|
RTK primary correction (single-base, VRS) operation time before Trimble xFill can be deployed |
Precise RTK for 10 minutes |
|
Convergence time once Trimble xFill is deployed |
Zero |
|
Maximum (primary correction) outage time |
5 minutes |
|
Typical horizontal precision1 |
RTK2 + 10 mm/minute RMS |
|
Typical vertical precision1 |
RTK2 + 20 mm/minute RMS |
1. Precisions depend on GNSS satellite availability. xFill positioning ends after five minutes of RTK outage.
2. RTK refers to the last reported precision before the correction source was lost and xFill started.