Understanding Generalized Surfaces
A surface is a 3D digital representation of topography, formed by a mesh of contiguous triangles, which is known as a triangulated irregular network (TIN). The triangles are connected at their vertices, which are defined by points with horizontal positions (X and Y values) and elevations (Z values). You can either import surfaces, or create them using existing data in your project.
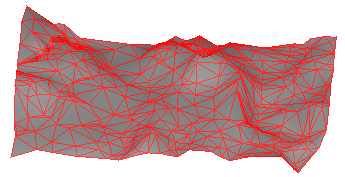
Use surfaces to:
- Visualize and analyze the topography at different construction phases (based on classifications):
- Compare one phase to another to generate volume reports for cut and fill earthwork operations.
- Represent stockpiles and depressions
- Create contour maps from topographic surveys.
- Upload a surface to a field device to check grades, or for accurate staking of an alignment or daylight boundary.