Intersection Island Properties
Island properties are set within properties for intersection legs. The following types of islands are supported:
- Drop Island
- Separator Island
- Turn Lane Island
- Double lane island (for twin intersections only)
- Roundabout Island
- Roundabout Contra Island
All types of islands have a set of general properties, but depending on which type of intersection is selected (Roundabout or T/X/Y), the available types of road islands will vary.
|
Selected Leg Island Properties In addition to the general island properties, each type has specific options. |
|
| Island general |
Type - None is the default for scenarios in which there is no island on the leg as it connects to the intersection/roundabout.
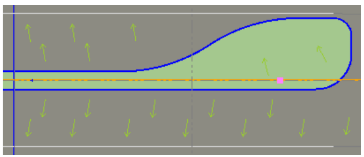
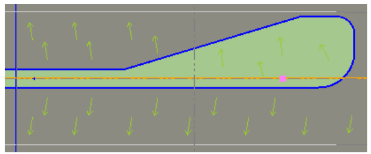
Continuous channeling: No - This is the default, which ends the island as the road edges become parallel (as shown below).
Yes - Select thisto continue the island parallel to the road edges (as shown below).
Slope reference - This determines where the top of the crown (reference of the slope) is located when a road island is inserted in the road leg geometry. The choice of this property has a large influence on the output of the 3D model (elevations in the intersection). Shoulder < > - This shows the width of the inner left/right shoulder, looking towards the center of the intersection. Walking path distance - This shows the distance from the front of the island to the beginning point of the pedestrian walking path. Length front - This shows the length of the side of the island that abuts the roundabout/intersection. Curb height - This shows the vertical distance from the flow line to the top of curb. Length expansion - This shows the size of the expansion at the back of the road island. |
| Island specific
(Roundabout island) |
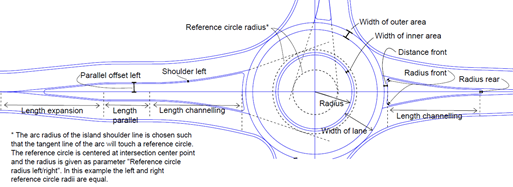
The illustration below shows all properties used to design a road island of the type 'Roundabout Island'.
Length expansion - This is the length of expansion at the back of the road island. Length channeling - This is the length of the front of the roundabout island where the island is widening out into the roundabout circular part. Length parallel - This is the length of the parallel part of the roundabout island. Radius front - This is the rounding value at the front of the roundabout island. Radius rear - This is the rounding value at the back of the roundabout island. The distance from the inner island (right side) - The direction of the front of the roundabout island's right side is handled by referring to a circle radius centered in the center point of the roundabout. The distance from the inner island (left side) - The direction of the front of the roundabout island's left side is handled by referring to a circle radius centered in the center point of the roundabout. Distance front - This is the distance from the outer radius of the roundabout to the front of the roundabout island. Parallel offset right - This is the offset to right side of the roundabout island in the back. Parallel offset left - This is the offset to left side of the roundabout island in the back. |
| Island specific
(Roundabout contra island) |
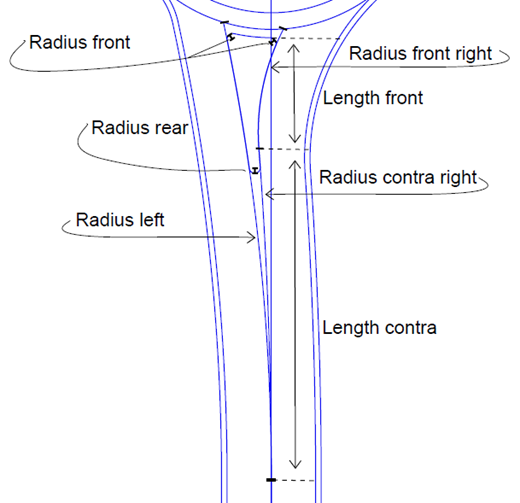
The illustration below shows all properties used to design the road island of the type 'Roundabout Contra Island'.
Length front - This is the length of the front part of the roundabout contra island where the island is widening out into the roundabout circular part. Corresponding to "Radius front right". Length contra - This is the length of the contra part of the roundabout contra island where the island turns to the left (contra). Length rear - This is the length of the rear part of the roundabout contra island, before the contra curve begins. Automatic computation of radii:
Radius front right - This is the radius used to compute the front of the right island, turning to the right after the contra curve. Radius contra right - This is the radius of the contra curve to the right side. Radius left - This is the radius of the contra curve to the left side. Reference circle radius right - This is used if Automatic computation of radii is set to Yes. Reference circle radius left - This is used if Automatic computation of radii is set to Yes. Distance front - This is the distance from the outer radius of the roundabout to the front of the roundabout island. Radius front - This is the rounding value at the front of the roundabout contra island. Radius rear - This is the rounding value at the back of the roundabout contra island. Length parallel - This is the length of the parallel part of the roundabout contra island. Parallel offset right - This is the offset to right side of the roundabout contra island in the back. Parallel offset left - This is the offset to left side of the roundabout contra island in the back. |
| Island specific
(Drop) |
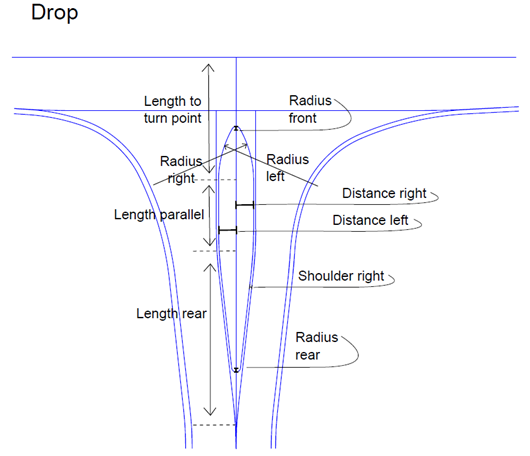
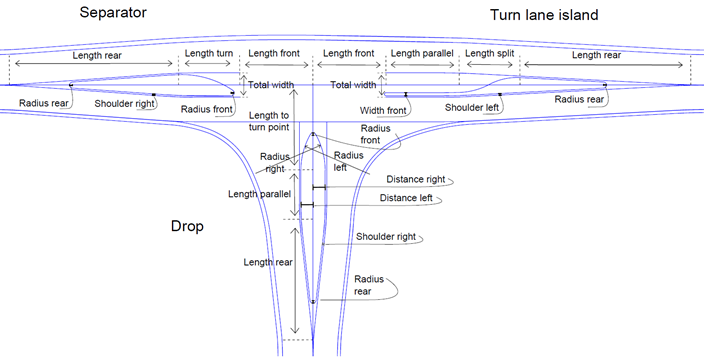
The illustration below shows all properties used to design the road island type "Drop".
Radius front - The rounding value at the front of the Drop. The default value is 0.5 meter. Radius rear - The rounding value at the back of the Drop. The default value is 0.5 meter. Radius left - The left side radius, turning to the right leg at the primary road. The default value is 12.0 meter. Radius right - The right side radius, turning to the left leg at the primary road. The default value is 12.0 meter. Distance left - The offset value of "Radius left" to compute the tangent point. The default value is 1.0 meter. Distance right - The offset value of "Radius right" to compute the tangent point. The default value is 1.0 meter. Length to turn point - The length from center point of the intersection to the tangent point of "Radius left/right". In this method both radius uses the same property. The default value is 12.0 meter. Length parallel - The Drop also can be computed with a parallel length (if wanted). The default value is 0.0 meter. Length rear - Length of expansion at the back of the Drop. The default value is 20.0 meter. |
| Island specific
(Separator) |
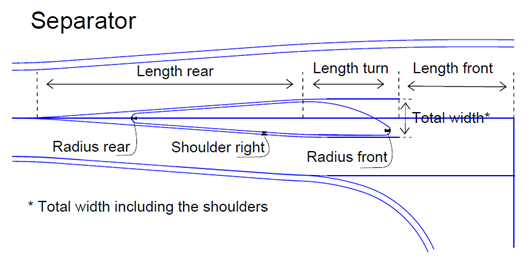
The illustration below shows all properties used to design the Road Island type 'Separator'.
Turn side - This property has 3 options;
These options direct the direction the island will turn – to left, to right or straight ahead. The illustration above shows this property = Right. The illustration below shows the property = Center.
Total width - This is the total width of the island area, which includes also the inner shoulder left/right. Eccentricity - The separator can be adjusted to both sides by a relative value, in the interval [0, 1]. 0 goes to the left and 1 goes to the right. Length turn - This is the length of the front of the separator. Radius front - This is the rounding value at the front of the separator. Radius rear - The rounding value at the back of the separator. Length rear - Length of expansion at the back of the separator. |
| Island specific
(Turn lane) |
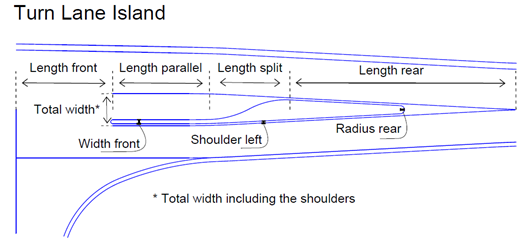
The illustration below shows all properties used to design the road island of the type 'Turn Lane'.
Turn side - This property has 2 options;
Total width - This is the total width of the island area, which includes also the inner shoulder left/right. Eccentricity - The separator can be adjusted to both sides by a relative value in the interval [0, 1]. 0 goes to the left and 1 goes to the right. Length parallel - This is the length of the parallel part of the turn lane, where vehicles wait before crossing the lane. Length split - This is the length of the split part of the turn lane, where the lane is split into another one (the left turn lane). Length rear - This is the length of expansion at the back of the separator. Width front - This is the width of the front of turn lane. This value is without the inner shoulders left/right. The default value is 0.5 meter. Radius rear - This is the rounding value at the back of the separator. |
| Island specific
(Double lane) |
Side - Specify the side where the island turns:
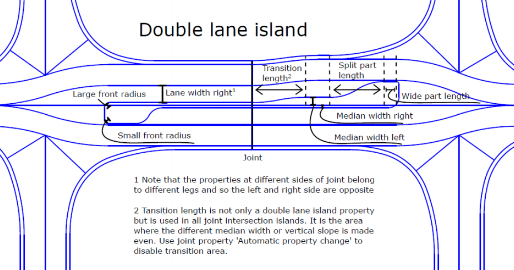
Total width - Shows the combined left and right widths. Median width left/right - This is the median offset to the left/right from the road leg. Lane width left/right - Specify the lane width left/right side. Wide part length - Specify the length of the front part of island where it is widest. The length is measured from the largest curved point of ‘Small Front Radius’ or ‘Large Front Radius’. Split part length - The length of the split part of island where it splits into two lanes. Small front radius - The radius in front of the island located to outer position. Large front radius - The radius in front of the island located to inner position. Note: If flags appear when you add a double lane island, review the errors in the Flags Pane, and make changes to the geometry by editing the Intersection Leg Properties in the Properties pane. |
| Island specific
(Joint) |
Transition length - The length of the joint location where geometry is transited from the island's internal geometry to the joint definition of the cross-section. Split Horizontal Method - The split of a lane can be computed in different ways. This method handles the horizontal part of the geometry. There are three methods;
Split Vertical Method - This method handles the vertical part of the split geometry. There are three methods;
Transition Horizontal Method - The horizontal transition to the joint can be computed in three different ways.
Transition Vertical Method - The vertical transition to the joint can be computed in three different ways.
Example of S curve method
Example of straight line method
The methods also apply in the vertical projection. |
|
Selected Road Intersection Leg Island Properties |
|
| Road intersection leg connection |
Main horizontal turning method - This method is called 'Touch roundabout double radius'. It computes a tangent point to the outer radius of the roundabout, by using the two radius values R1-R2 (Turn radius 1 – Turn radius 2). Main vertical turning method - The vertical method is called 'Copy'. The method connects the vertical alignment to the elevation of the outer roundabout at the tangent point. No other methods are available in this case. |