Intersection Turn Lane Properties
Turn lane properties are set within properties for intersection connections. The following types of turn lanes are supported:
- Turn lane (normal)
- Turn lane short
|
Selected Turn Lane Properties |
|
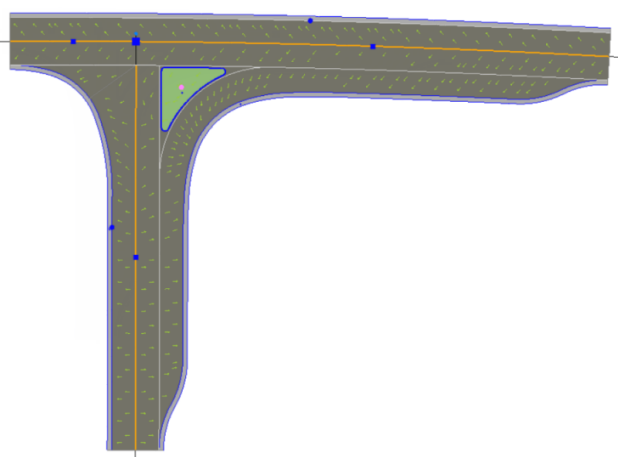
Traditional T- X or Y Intersection |
|
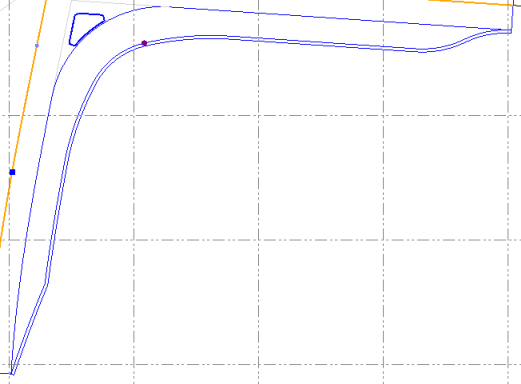
Horizontal turning method - To compute a turn lane to a leg connection, chose Turn lane in the Horizontal turning method list; the geometry will be computed.
Compute interpolation line - Line work in a turn lane The primary output of a road turn computation consists of 3D lines describing all breaklines of the right turn:
In addition, the shoulder to the right line is also computed in the traditional leg connection geometry.
Properties
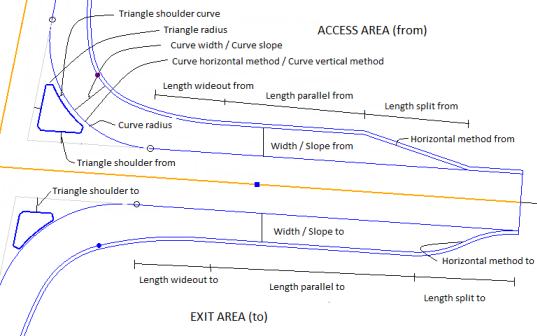
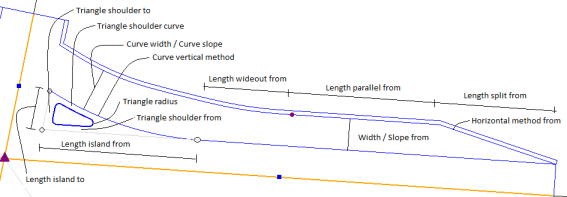
Triangle radius - The rounding radius of the triangle island. Use the same value for all three corners. Triangle shoulder from - The shoulder to triangle island on the ‘from’ side (access). Triangle shoulder to - The shoulder to triangle island on the ‘to’ side (exit). Triangle shoulder curve - Shoulder to triangle island on the ‘curve’ side. Length wideout from - The width of the lane in the curve is normally wider than at the access (and exit) part of the right turn. To widen the lane into the curve, it has to start before the curve point of the curve, in order to handle the change of width over some distance. Length parallel from - The length of the lane where the access lane width is constant. Length split from - The length where the lane is spilt from the basic road leg lane at the access part. The split can be computed by three different methods (see Horizontal method from). Horizontal method from - There are three different methods at the access part of right turn;
Transition factor from - Width from - The width of the lane (access part of right turn). Slope from - The slope of the lane (access part of right turn). Curve radius - The radius of the curve to the right turn. This radius can be used in several methods of computing the right turn's left side geometry. This version supports two methods (see Curve horizontal method). Curve width - The width of the lane in the curve area. Curve slope - The slope of the lane in the curve area. Curve horizontal method - Three methods are supported;
Curve vertical method - Two methods are supported;
Length wideout to - The width of the lane in the curve is normally wider than at the exit (and similar to the access) part of the right turn. To widen the lane from the curve and into the exit area, it has to end after the curve point of the curve in order to handle the change of width over some distance. Length parallel to - The length of the lane where the exit lane width is constant. Length split to - The length where the lane is spilt from the basic road leg lane at the exit part. The split can be computed by three different methods (see Horizontal method from). Horizontal method to - There are three different methods at the exit part of right turn;
Width to - The width of the lane (exit part of right turn). Slope to - The slope of the lane (exit part of right turn). Curb height - This shows the vertical distance from the flow line to the top of curb.
|
|
Traditional T- X or Y with Right Turn Short |
|
Horizontal turning method - To compute a short turn lane to a leg connection, choose the Turn Lane Short option from the Horizontal turning method list; the geometry will be computed. Turn Lane Short is a simplified version of Turn Lane, where the exit parameters are omitted.
Linework in Turn Lane Short Turn Lane Short has identical output as a turn lane, which means the linework has the same structure. The primary output consists of these 3D lines:
In addition, the shoulder to the right line is also computed in the traditional leg connection geometry.
Properties
Triangle radius - This is the rounding radius of triangle island. Use the same value for all three corners. Triangle shoulder from - This is the shoulder to triangle island on the ‘from’ side (access). Triangle shoulder to - This is the shoulder to triangle island on the ‘to’ side (exit). Triangle shoulder curve - This is the shoulder to triangle island on the ‘curve’ side. Length wide out from - The width of the lane in the curve is normally wider than at the access (and exit) part of the right turn. To widen the lane into the curve, it has to start before the curve point of the curve in order to handle the change of width over some distance. Length parallel from - The length of the lane where the access lane width is constant. Length split from - The length where the lane is spilt from basic road leg lane at the access part. The split can be computed by three different methods (see Horizontal method from). Horizontal method from - There are three different methods at the access part of right turn;
Width from - This is the width of the lane (access part of right turn). Slope from - This is the slope of the lane (access part of right turn). Curve width - This is the width of the lane in the curve area. Curve slope - This is the slope of the lane in the curve area. Curve vertical method - There are two methods supported;
Radius to - Length island from - This is the length from where the curve radius starts at the access part of the from-leg. Length island to - This is the length from where the curve radius ends at the exit part of the to-leg. Curb height - This shows the vertical distance from the flow line to the top of curb. |
|
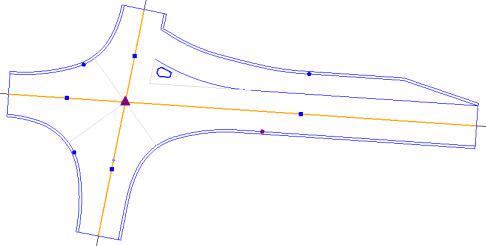
Roundabout Intersection |
|
Lane offset - Specify the distance from outer radius of the roundabout to the tangent point of the turn lane. If the value is less than 1.0 meter, you will need to change other properties to get the program to compute the curb. |